How to Create an International Employee Handbook
Creating a consistent and comprehensive employee handbook is crucial for any company, especially when operating across multiple countries. An international employee handbook is a document that outlines the policies, procedures, and expectations for employees across all locations where your company operates. Unlike a standard employee handbook, which focuses on a single country’s laws and practices, an international handbook is designed to address the diverse legal and cultural requirements of multiple regions.
In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about developing an international employee handbook. You’ll learn what it is, why it’s important, and how it can benefit your organization. By the end of this article, you’ll understand the steps involved in creating a handbook that not only meets legal requirements but also respects cultural differences and aligns with your company’s values.
Why Your Company May Need One
Having an international employee handbook offers several key benefits. First, it provides a unified set of guidelines that apply to all employees, helping to maintain consistency across different locations. This can be particularly important for companies with a global workforce, where differences in local laws and customs can create confusion if not properly addressed.
Second, an international handbook is adaptable. It allows you to tailor policies to meet the specific needs of each region while still maintaining a consistent overall approach. This flexibility helps ensure compliance with local regulations and shows respect for cultural differences.
Without an international employee handbook, companies often face challenges such as inconsistent policy enforcement, legal risks, and cultural misunderstandings. These issues can lead to employee dissatisfaction, legal complications, and a fragmented company culture. By creating a well-structured international employee handbook, you can avoid these problems and build a stronger, more cohesive organization.
Understanding Legal and Cultural Differences
When creating an international employee handbook, it’s important to recognize and address the legal and cultural differences across the countries where your company operates. This section will guide you through the key areas to focus on, making your handbook both legally compliant and culturally sensitive.
Navigating Legal Requirements
Every country has its own set of labor laws and regulations that companies must follow. These laws cover various aspects of employment, such as working hours, minimum wage, benefits, and employee rights. When you operate in multiple countries, it’s essential to understand the specific legal requirements in each location to ensure your handbook complies with local laws.

Using a standard U.S. employment handbook in other countries can lead to issues, as it might unintentionally apply U.S.-specific protections that aren’t relevant elsewhere. For example, Title VII protections in the U.S. don’t cover other important legal rights that might exist in the EU or other regions. In countries like Japan, France, and Belgium, employers are required to publish mandatory “work rules,” which are heavily regulated and leave little room for flexibility. Additionally, ensuring that your handbook is translated correctly and complies with local language requirements is crucial.
Start by researching the labor laws in each country where you have employees. This includes understanding regulations related to hiring, termination, working conditions, and employee benefits. It’s also important to keep track of any changes in these laws, as non-compliance can lead to legal penalties and damage your company’s reputation.
To effectively manage these legal differences, consider working with your international HR team and local legal experts or HR professionals who are familiar with the laws in each country. They can help you draft sections of your handbook that meet local requirements while aligning with your company’s global policies.
Cultural Sensitivity and Inclusion
Cultural differences can significantly impact how workplace policies are perceived and implemented. What is acceptable in one country might not be in another, and a one-size-fits-all approach may lead to misunderstandings or even conflicts.
To create a culturally sensitive and inclusive handbook, start by understanding the cultural norms and values in each country where you operate. This includes being aware of local customs, communication styles, and expectations regarding work-life balance, hierarchy, and decision-making.
Addressing Cultural Differences in Workplace Policies
For instance, in Spain, some regions still observe mid-day siestas, which might require adjustments in your working hour policies. In New Zealand, some employers are experimenting with four-day workweeks, reflecting a cultural shift that might influence your future business model. While these practices are not mandatory, being aware of such cultural nuances can help you craft policies that align with local expectations and keep employees engaged.
Incorporate this understanding into your handbook by adapting policies to respect these cultural differences. Other examples include considering how holidays are observed, how dress codes are perceived, and how communication should be handled in different regions. By doing so, you can create a workplace environment that feels inclusive and respectful to all employees, regardless of their location.
To further promote inclusion, involve local employees in the process of developing the handbook. Their insights can help you identify potential cultural pitfalls and ensure that the handbook reflects the values and needs of your global workforce. Additionally, providing diversity and inclusion training can help employees understand and respect each other’s cultural backgrounds, fostering a more harmonious work environment.
By carefully navigating legal requirements and cultural differences, you can create an international employee handbook that not only meets the necessary legal standards but also promotes a positive and inclusive company culture across all your locations.
Essential Components of an International Employee Handbook
Creating an international employee handbook requires careful consideration of various essential components. These components ensure that the handbook is comprehensive, legally compliant, and culturally appropriate for all employees across different locations. In this section, we’ll cover the key elements that should be included in your handbook.
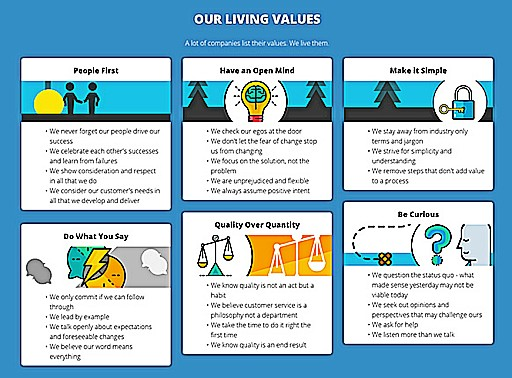
Company Values and Mission
Start by clearly stating your company’s values and mission. These should reflect both your global objectives and the unique values of the regions where you operate. It’s important to align your global company values with local practices, ensuring that all employees, regardless of location, understand and support the company’s mission. This alignment helps create a unified company culture across all locations.
Employment Policies
Employment policies are the backbone of your employee handbook. These policies outline the rules and expectations for all employees. While some policies should be standardized globally, others may need to be adapted to meet local requirements.
Key policies to include are:
- Working Hours: Define standard working hours and any variations based on local laws.
- Holidays: List global holidays and allow for local holiday observances.
- Leave Policies: Specify different types of leave, such as vacation, sick leave, and parental leave, and how they apply in each country.
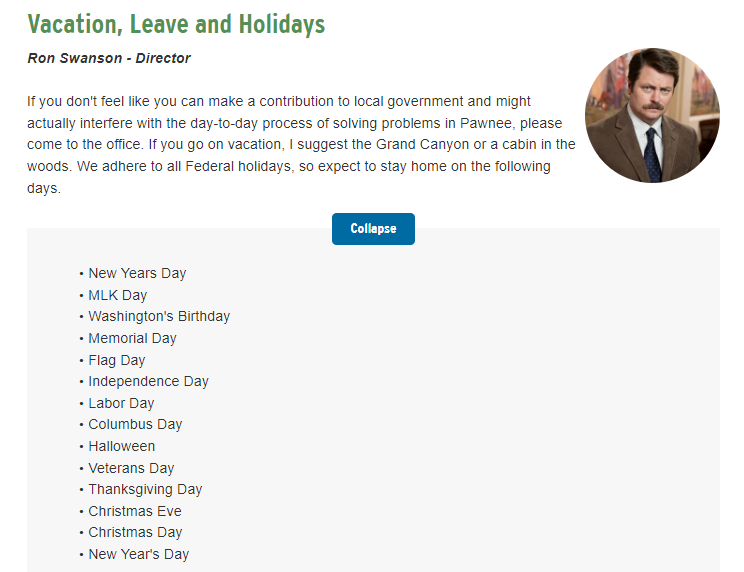
By balancing global consistency with local flexibility, you ensure that your employment policies are fair and relevant in every region.
Compensation and Benefits
Compensation and benefits are critical to employee satisfaction. Your handbook should provide guidelines for offering equitable compensation packages that consider local market conditions, cost of living, and legal requirements.
Tailor benefits to meet local expectations and standards. For example, health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks might vary widely between countries. Make sure your compensation and benefits packages are competitive in each region while maintaining overall consistency across the company.
Code of Conduct and Ethics
A code of conduct outlines acceptable behavior and ethical standards for all employees. This section should clearly define what is expected of employees in terms of professionalism, integrity, and respect for others.

Address issues such as discrimination, harassment, and workplace safety in a way that considers both global standards and local cultural norms. This helps create a respectful and safe working environment for everyone, regardless of where they are located.
Health, Safety, and Wellness
Health and safety are top priorities in any workplace. Your handbook should outline global health and safety standards that apply to all locations. Additionally, include any specific local regulations or practices that employees need to follow.
Promote employee wellness by offering programs or resources that support physical and mental health. These initiatives can be adapted to fit local needs and preferences, helping to foster a healthy and productive workforce.
Remote Work and Digital Communication
With the rise of remote work, it’s important to include policies for managing a distributed workforce. Clearly define expectations for remote work, including work hours, communication protocols, and data security practices.
Provide guidelines for effective digital communication across time zones and cultures. This can include recommended tools for collaboration, tips for clear and respectful communication, and procedures for virtual meetings. These policies help ensure that all employees stay connected and productive, no matter where they work.
By including these essential components in your international employee handbook, you’ll create a comprehensive guide that supports your global workforce while respecting local differences.
Steps to Create an International Employee Handbook
This process involves several important steps. Each step helps make sure the handbook meets legal requirements and respects cultural differences at the same time. Here’s how you can go about it:
Step 1: Research and Gather Information
Start by researching the legal, cultural, and operational needs of the regions where your company operates. Identify the local labor laws, cultural norms, and any specific operational requirements that need to be addressed in your handbook. This information will serve as the foundation for creating a handbook that is both compliant and relevant in each location.
Step 2: Collaborate with Local Experts
Once you have gathered the necessary information, collaborate with local HR teams and legal advisors in each country. These experts have a deep understanding of local laws and cultural practices, which is crucial for ensuring that your handbook is accurate and effective. Their insights will help you avoid potential legal pitfalls and cultural misunderstandings.
Step 3: Draft the Global Framework
With input from local experts, draft a global framework for your employee handbook. This framework should include standardized policies and guidelines that apply to all employees, regardless of location. The framework should be flexible enough to allow for customization based on local needs while maintaining overall consistency across the company.
Blissbook’s Personalized Content Feature
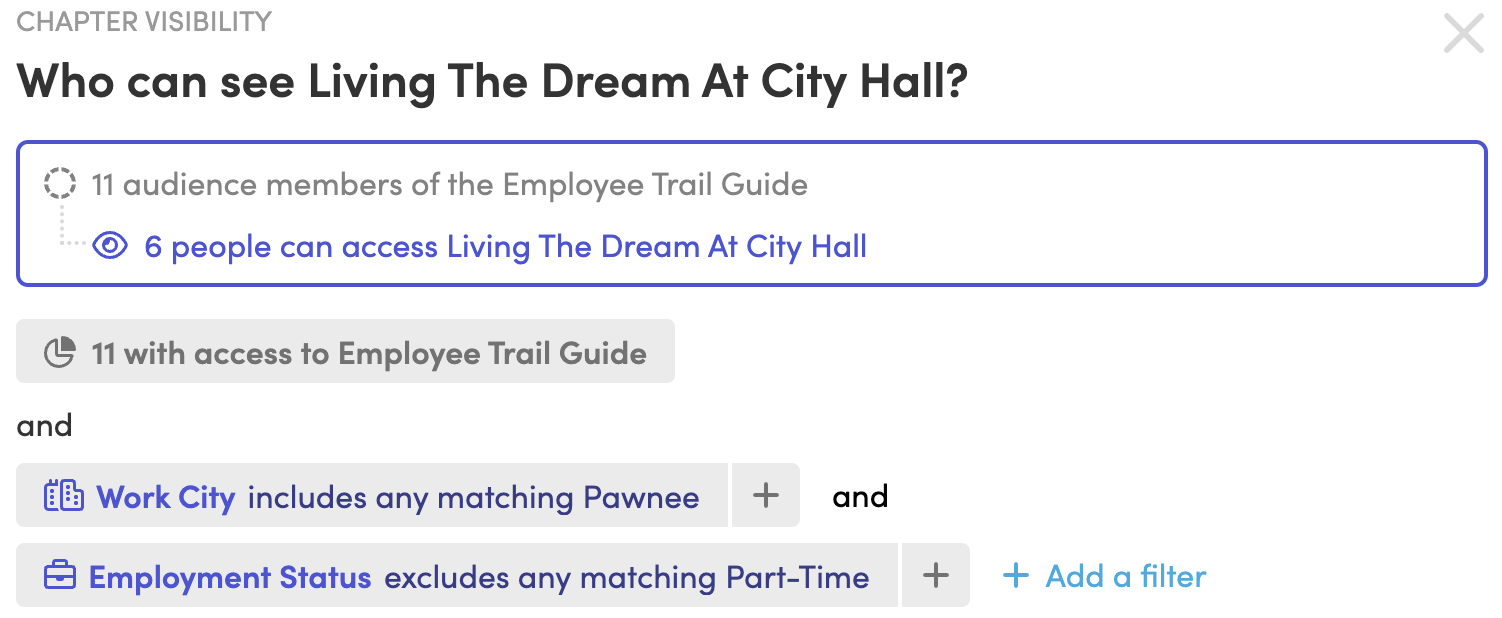
Simplify and consolidate multiple handbooks and policies into one seamless, personalized experience. Employees will log in and see only the content that’s relevant to them, making it easier to access and increasing their engagement. Blissbook’s personalized content feature allows you to target specific content to certain groups. For instance, if you need specific information to be directed only at employees in Spain, you can easily set it up so that only they will see that content.
Step 4: Localize Content
After drafting the global framework, tailor the content to meet the specific legal and cultural requirements of each region. This may involve adjusting policies to comply with local labor laws, incorporating cultural norms, and addressing any region-specific operational needs. Localization ensures that your handbook is relevant and effective in each location.
Blissbook’s Personalized Content Feature
If your handbook includes information that only applies to certain employees or if you’re currently managing multiple handbooks to address slight variations for different groups, Blissbook’s Personalized Content feature is your solution. You can centralize everything in one place, whether it’s a large addendum, a specific policy, or just a particular section of content. This feature lets you edit everything from one central location, eliminating the need to update the same information in multiple documents. It also ensures that employees can easily find the content that’s relevant to them within a single handbook.

Multiple Languages Feature
Blissbook offers a variety of solutions for managing multiple languages or non-English content to help you achieve your project goals. These options differ in terms of complexity, size, and functionality. Here are the three available options:
- PDF Embed
One approach is to translate your document into the desired language outside of Blissbook and then embed the translated version as a PDF within your primary language document. This is an ideal choice if your translations are already in PDF format and you prefer to keep them that way. - Separate Documents:
Another option is to create separate documents for each language within Blissbook, where you can assign a specific language to each document. - Multiple Languages in One Document:
The final option allows you to incorporate multiple languages within a single handbook. You can assign different languages to individual sections, and users will see a language selector when they access the document. They can choose their preferred language for viewing the content. Since it’s all within one document, users only need to sign once, and you can manage and report on it from one place.
Step 5: Review and Revise
Before finalizing the handbook, involve your global HR teams in the review process. Their feedback is valuable in ensuring that the handbook is both practical and compliant across all regions. Make any necessary revisions to address their concerns and ensure that the handbook maintains consistency while meeting local requirements.
Step 6: Implementation and Communication
Once the handbook is finalized, develop a strategy for rolling it out across your global offices. This includes training and educating employees on the content of the handbook to ensure they understand the policies and guidelines. Clear communication is key to successful implementation, so make sure that all employees have access to the handbook and know where to find the information they need.
By following these steps, you can create an international employee handbook that meets the diverse needs of your global workforce.
Tips for Updating and Maintaining Your Handbook
Keeping your international employee handbook up to date is important for its effectiveness. Here are some tips on how to regularly review and update it to guarantee it remains relevant and useful.
Regular Reviews and Audits
Set up a schedule for regular reviews of your handbook. This could be annually or semi-annually, depending on how often there are changes in laws or company policies. Regular reviews help you identify any outdated information and make the necessary updates. By doing this, you ensure that the handbook continues to comply with legal requirements and reflects the latest company policies.
As laws and company policies evolve, it’s important to adjust the handbook accordingly. Regular audits allow you to stay on top of these changes and keep your handbook accurate and reliable for all employees.
Employee Feedback and Engagement
Encourage employees to provide feedback on the handbook’s content. They are the ones using it daily, so their input is valuable in identifying areas that may need improvement or clarification. Regularly seek out their opinions through surveys, meetings, or suggestion boxes.
Use this feedback to adapt policies based on practical experiences. If employees find certain policies unclear or difficult to follow, consider revising those sections to make them more user-friendly. Engaging employees in the process not only improves the handbook but also increases their commitment to following the guidelines.
Final Thoughts
An international employee handbook is a vital tool for any company operating across multiple countries. It ensures that all employees, regardless of location, understand your company’s policies, values, and expectations. By creating a comprehensive and culturally sensitive handbook, you help maintain consistency, comply with local laws, and foster a positive work environment for your global workforce.
To keep your handbook effective, it’s essential to regularly review and update it, incorporating employee feedback and adapting to changes in laws and company policies. A well-maintained handbook not only supports your employees but also strengthens your company’s culture and operations worldwide.
If your business hasn’t yet created or updated its international employee handbook, now is the time to take action. With Blissbook, you can easily design, customize, and manage your handbook to meet the unique needs of your global workforce.
Start today by setting up a trial to create your handbook using Blissbook, and see how Blissbook can simplify the process and help you build a handbook that works for your entire organization.